언제쯤 코로나 바이러스 치료제가 나올까?
- 바이러스 생활경로별 개발전략을 중심으로
(재)범부처신약개발사업단 사업개발팀
Ⅰ. 글로벌 치료제 개발 동향
코로나19 바이러스(2019-nCoV, SARS-CoV-2; COVID-19을 유발하는 바이러스)는 숙주세포에 있는 수용체를 통해 세포내로 들어가 자가 복제를 한다. 복제가 진행되는 동안에는 숙주세포의 선천면역 기능을 교란하여 면역회피를 시도한다. 생산된 virion들은 결국 세포 밖으로 방출되어 면역반응을 일으킨다. 연령별로 사망자를 보면 면역반응이 너무 강하거나(젊은 성인), 약하면 (노인) 치사율이 높고 보통의 면역상태인 소아의 경우는 치사율이 낮음을 보인다.
코로나19의 염기서열은 알려져 있지만 단백질 구조는 제한된 범위에서 알려져 있다. 하지만, 코로나 19와 SARS-CoV는 염기서열이 80% 정도 일치하고, SARS-CoV의 단백질 구조는 대부분 밝혀져 있기 때문에 코로나19의 3차원 구조를 SARS-CoV를 통해 유추할 수 있다(Ref 1).
코로나19 바이러스는 plus strand enveloped RNA virus이다. 코로나 바이러스과에 속하는 전체 바이러스에 걸쳐서 highly conserved된 Polyprotein은 스스로 절단되어 16개의 nonstructural 단백질을 생성한다. 그리고 Structural 단백질로는 Spike (S) 단백질, Envelope (E) 단백질, Membrane (M) 단백질, Nucleocapsid (N)이 있다.
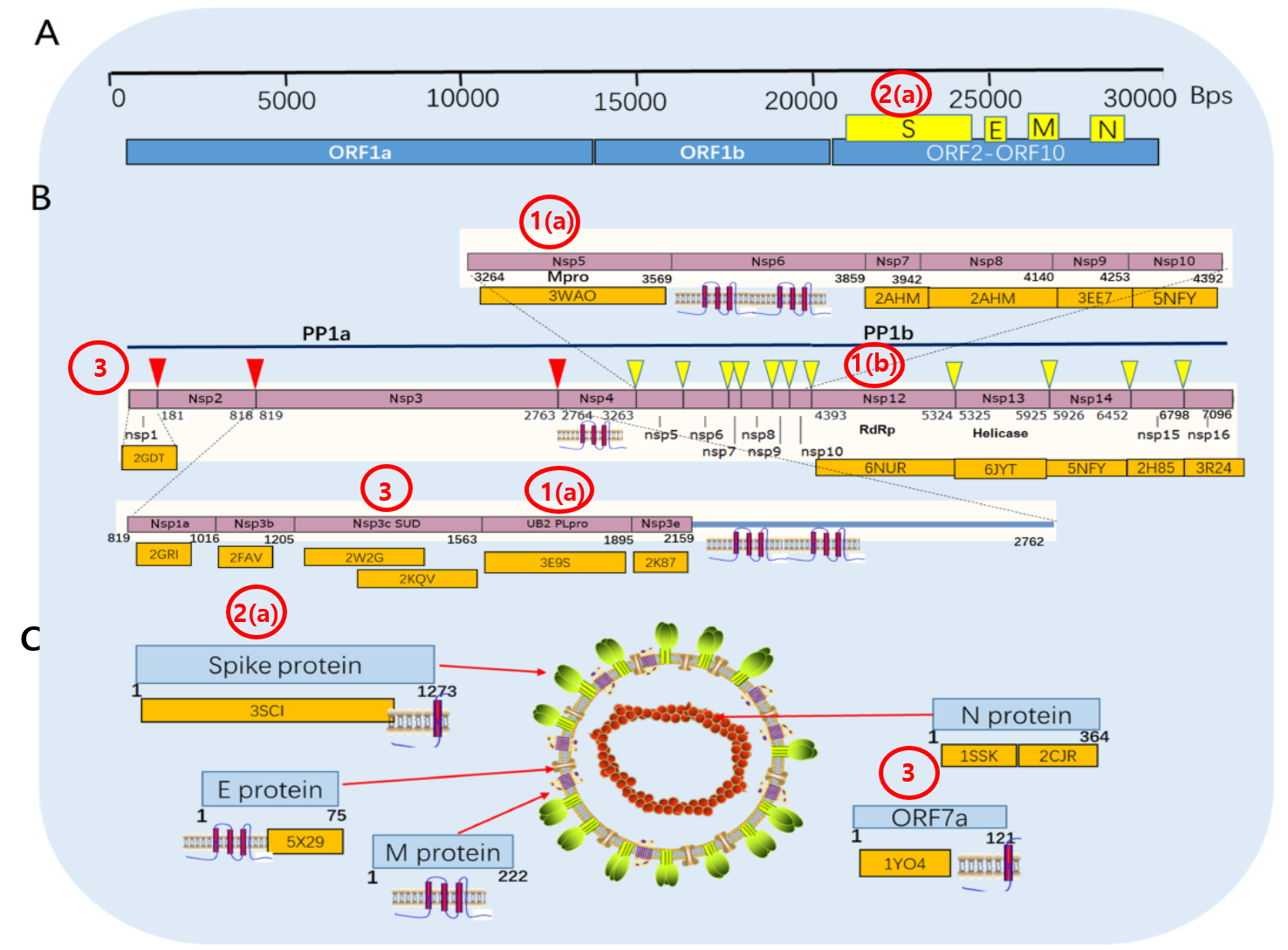
Figure 1. 코로나19 전체 지놈과 그 단백질 분석표(Ref 1)
(A) SARS-CoV-2의 지놈 모식도
(B) 거대한 replicase polyprotein PP1ab
7096개의 아미노산으로 이루어진 PP1ab 단백질은 보라색 사각형으로 표시함. 빨간색 삼각형은 PLpro에 의해 절단되는 부위이고 노란색 삼각형은 3CLpro에 의해 절단되는 부위. 보라색 사각형 밑에 있는 숫자는 개별 단백질이나 부위가 끝나는 아미노산의 위치임. 개별 단백질 또는 부위 밑에 있는 오렌지색 사각형은 3차원 구조가 판독된 경우에 표시됨.
(C) 코로나 바이러스가 가진 4가지 구조 단백질의 모식도. S, spike; E, envelope; M, membrane; N, nucleocapsid.
* 본문에서 언급한 치료제 타겟 단백질을 빨간색 타원안에 빨간색 숫자로 표시함(숙주세포 제외)
코로나 바이러스 치료제 개발전략은 바이러스 생존 경로별로 구분이 가능하다.
|
생활경로 |
기능 |
타겟 |
|
1. 합성과 복제 |
1 (a) Protease |
Papain Like protease (PLpro), Mainprotease (Nsp5또는 3CLpro) |
|
1 (b) 중합효소 |
RNA-dependent RNA Polymerase (Nsp12또는 RdRp) |
|
|
2. 바이러스가 숙주세포의 수용체에 결합하는 단계 |
2 (a) 바이러스 구조 단백질 |
Spike 단백질 |
|
2 (b) 숙주세포 특이적 수용체나 효소 |
human ACE2, type-IItransmembraneserineprotease (TMPRSS2) |
|
|
3. virulence factor에 작용하여 숙주의 선천면역을 회복시키는 약물 |
|
Nsp1, Nsp3c, ORF7a |
(1) 바이러스 복제에 필수적인 효소에 작용하여 그 합성과 복제를 저해하는 치료제로 (a) Protease 타겟으로는 Papain Like protease (PLpro), Main protease (Nsp5 또는 3CLpro) 두가지가, (b) 중합효소 타겟으로는 RNA-dependent RNA Polymerase (Nsp12 또는 RdRp)가 있다
(2) 바이러스가 숙주세포의 수용체에 결합하는 단계를 방해하는 치료제로 (a) 바이러스 구조 단백질 타겟으로는 Spike 단백질이 있고, (b) 숙주세포 특이적 수용체나 효소에 작용하여 바이러스가 숙주세포안으로 진입하는 것을 막는 타겟으로는 human ACE2와 type-II transmembrane serine protease (TMPRSS2)가 있다.
(3) virulence factor에 작용하여 숙주의 선천면역을 회복시키는 약물로 그 타겟으로는 Nsp1, Nsp3c, ORF7a가 있다.
이 개별 경로와 타겟별로 약물 개발동향을 살펴보고자 한다.
1) 바이러스 복제를 막는 기전
그 중에서 가장 빨리 코로나 치료제로 승인을 받을 가능성이 있는 Repurposing Drug Pipeline은 아래와 같이 정리될 수 있다. 이 파이프라인들은 이미 승인되었거나 혹은 임상연구 결과를 가진 항바이러스 치료제를 repurposing 하여 금년 4월 말까지 임상 결과를 확인할 수 있는 순으로 정리했다(Table 1, Ref 2).
그 중에서 가장 주목을 받고 있는 제품으로는 렘데시비르가 있다. 렘데시비르는 원래 Ebola 바이러스 치료제로 개발되어 2018년 임상2상을 진행한 결과 항체 치료제 대비 효능이 높지 않아서 개발이 중단되었던 물질이다. 코로나 19 바이러스 유전자 염기서열과 80% 의 염기서열 유사성이 있는 SARS-CoV의 단백질 구조를 활용한 계산화학적인 분석 결과에 따르면 RdRp, TMPRSS2에 동시에 결합해서 바이러스 자기복제를 억제하거나 바이러스의 인체내 침입을 막을 수 있는 가능성이 있는 것으로 알려져 있다(Ref 1).
RdRp를 타겟하는 다른 약물인 Favipiravir(아비간)은 중국 과기부 관리의 발표에 따르면 340명의 환자가 참여한 임상시험에서 긍정적인 결과를 보였다. 코로나 바이러스 감염자 중 비투약군에서는 양성에서 음성으로 회복되는데 걸리는 시간이 11일인데 반해서 투약군에서는 평균 4일만에 회복되었다. 폐의 건강상태를 엑스선으로 확인한 결과 비투약군에서 폐 상태 호전도가 61%에 그친 반면에 favipiravir를 투약받은 환자에서는 91%가 호전되었다. 하지만 favipiravir를 중증환자에 투약할 경우에는 효과가 크지 않았다고 보도되었다(Ref 3).
Table1에는 포함되어 있지 않지만 그중 Protease를 타겟하는 칼레트라 연구결과 역시 발표되었다. 코로나19에 감염된 199명의 중증환자를 표준치료군 100명, 칼레트라 투여군 99명으로 나누어 임상시험을 진행했는데, 표준치료는 항생제투여, 산소호흡기 등을 사용했다. 하지만 표준치료군과 칼레트라 투여군 사이에 임상적 개선을 보이는 시간이나 치사율의 차이는 없었다(Ref 4). 계산화학적 Docking 모델에 따르면 칼레트라(로피나비르+리토나비르)는 코로나 바이러스 치료제 개발에서 중요한 타겟인 3CLpro, PLpro, RdRp에 모두 결합하지 않는 것으로 분석되었다(Ref 1).
일반인에게 잘 알려진 클로로퀸의 정확한 작용기전은 아직까지 알려져 있지 않지만 항바이러스 치료제로 1935년에 승인되었다. 클로로퀸은 Azithromycin와 병용투여시 좀더 효과가 좋은 것으로 알려져 있으나, 동시에 눈과 신장에 대한 부작용 우려가 보고된 바 있다. 이와 관련하여 코로나 19바이러스를 in vitro에서 실험하여 클로로퀸(chloroquine)과 렘데시비르(remdesvir), 그리고 파비피라비르(favipiravir)의 EC50를 측정한 결과가 발표되었다. 렘데시비르에서 EC50은 0.77μM, 클로로퀸에서 EC50은 1.13μM, 파비피라비르 EC50는 61.88μM로 측정되었다(Ref 5).
|
생존 경로 구분 |
Intervention |
Type |
Target * |
EC50 (uM) ** |
EC50 |
Comparator |
Sponsor |
Phase |
End date |
Trial ID |
|
|
Hydroxychloroquine |
Antimalarial |
Duffy antigen chemokine receptor(ACKR1)modulator |
1.13 (Chloroquine) |
3 uM (Malaria) 0.72 ~ 1.13 uM (Corona 19) |
Placebo |
Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University |
Ph IV |
2/29/2020 |
ChiCTR2000029559 |
|
1 (a) + 면역조절 |
Ebastine; Lopinavir; Interferon α |
Mucolytic; Antiviral |
HIV protease inhibitor (Lopinavir) |
|
|
Lopinavir; Interferon α |
Wuhan Red Cross Hospital |
Ph IV |
3/30/2020 |
ChiCTR2000030535 |
|
1 (a) + 면역조절 |
Danoprevir; Ritonavir; Interferon |
Antiviral |
HIV protease inhibitor (Ritonavir) |
|
|
Lopinavir/ritonavir; Pegasys; Novaferon; Chinese medicines + interferon (4 arms) |
The Ninth Hospital of Nanchang; Ascletis Pharmaceuticals |
Ph IV |
3/31/2020 |
NCT04291729 |
|
1 (b) |
Remdesivir |
Antiviral |
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) |
0.77 |
12 nM (Ebola) |
Placebo |
Capital Medical University; Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences; China-Japan Friendship Hospital |
Ph III |
4/10/2020 |
NCT04252664 |
|
1 (b) |
Favipiravir |
Antiviral |
Favipiravir (T-705) is a novel viral RNA polymerase inhibitor, it is phosphoribosylated by cellular enzymes to its active form, Favipiravir-ribofuranosyl-5′-triphosphate (RTP). Favipiravir-RTP inhibits the influenza viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP) activity. |
61.88 |
39 uM (H5N6 Influenza A) |
High, middle, and low doses (3 arms) |
Beijing Chaoyang Hospital, Capital Medical University |
Ph II |
4/20/2020 |
ChiCTR2000029996 |
Table 1. 코로나19에 대하여 Repurposed 된 임상시험 약물 사례들과 타임라인. (Ref 1*, 2, 5** in vitro 실험결과)
2) 바이러스의 세포내 진입을 막는 기전
다음으로, 바이러스의 세포내로의 진입을 막는 개발 전략을 살펴보자.
코로나19는 당쇄가 촘촘하게 결합된 스파이크(Spike, S) 단백질을 통해 숙주세포로 진입한다. S 단백질은 trimer로 존재하며 (Fig 2) 그 중 S단백질의 up 된 RBD (Receptor Binding Domain)을 통해 숙주세포의 수용체에 결합한다. (Ref 6)
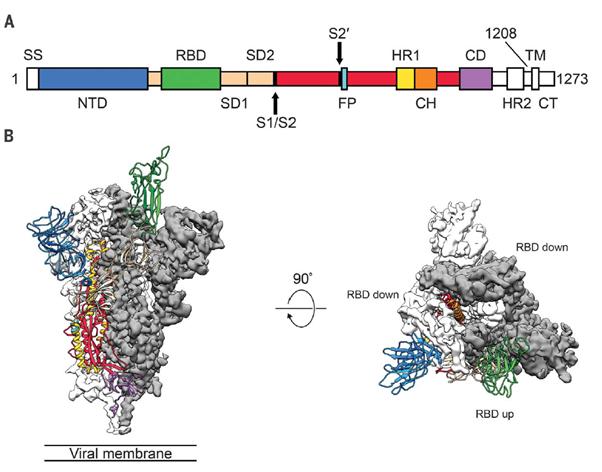
Fig 2. 코로나 19 S 단백질의 Prefusion 상태의 구조 (Ref 6)
(A) 색상으로 부위별 기본구조가 모식화 된 코로나19 S 단백질. 단백질 발현 construct에서 제외되었거나 시각화 되기 어려운 부분은 하얀색. SS, 시그널 서열; S2′, S2′ 단백질 절단 부위; FP, fusion 펩타이드; HR1, heptad repeat 1; CH, 센트럴 헬릭스; CD, 커넥터 도메인; HR2, heptad repeat 2; TM, 막투과 부위; CT, cytoplasmic tail. 화살표는 단백질 절단부위.
(B) 단일 RBD up상태(녹색 리본)인 코로나19 S 단백질 접합이전 (prefusion) 상태의 측면도와 평면도. 두개의 RBD down된 protomer는 cryo-EM 밀도로 흰색이나 회색으로 표시된 반면, RBD up protomer는 (A)에 따라 색상으로 표시됨.
코로나 19의 RBD는 기존의 SARS와 공통되는 부분과 차이가 나는 부분이 있다. 적색으로 표시된 차이가 나는 부분, 특히 ACE2 결합부위가 중요한 약물개발 타겟으로 사용될 수 있다 (Fig 3). 특히, 코로나19의 Envelope에 돌출되어 있는 스파이크 단백질(Spike protein: S)은 숙주세포의 수용체인 ACE-2 (Angiotension converting enzyme 2)에 결합하여 세포 안으로 진입한다. ACE2 근처에 있는 Serine protease인 TMPRSS2가 S단백질을 절단시켜 활성화시킨다. ACE2 또는 TMPRSS2와 S단백질의 결합을 저해하는 물질이 있으면 약물로 시험할 수 있다.
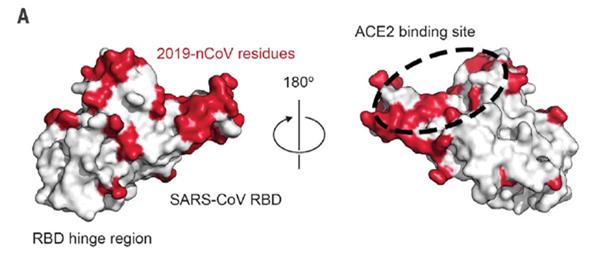
Fig 3. SARS와 코로나19의 RBD 부위 중 공통되는 부분 (흰색)과 차이가 나는 부분 (적색) (Ref 6)
중국 연구자들의 계산화학적 docking model에 따르면 Spike와 ACE2의 결합 인터페이스에 유일하게 결합하는 물질은 광귤 (bitter orange, Citrus aurantium)에 포함되어 있는 hesperidin이다(Fig 4).
또한, 일본에서 췌장염 치료제로 임상 승인된 TMPRSS2 저해제인 Camostat이 바이러스 진입을 저해하는 실험결과가 발표되었는데 이 역시 약물개발 전략 2 (b) 경로를 따른 치료제 개발 가능성을 시사한다(Ref 7).
ACE2나 TMPRSS2는 바이러스의 인체내 침입을 억제할 수 있는 주요 타겟으로 비록 개발 및 시판승인까지 소요되는 시간이 길기는 하지만 향후 백신과 중화 단클론 항체 개발 등 약물개발의 타겟으로 중요하다. 항체나 백신을 통해 바이러스 치료제를 개발할 경우 비임상 단계를 포함 전체 임상연구 기간이 아무리 빨라도 최소 1년 이상은 소요될 수밖에 없어서 대개는 중도에 개발을 포기하는 사례가 많다. 다만 코로나 바이러스가 계절적 유행병으로 변할 경우에는 백신이나 항체 치료제 개발전략 역시 필요할 것이다.
백신의 경우 바이러스 또는 그 일부인 subunit을 단백질 또는 이를 생성할 수 있는 핵산의 형태로 인체에 주입하여 면역체계가 항체를 생성하도록 하는 예방 및 치료법이다. 그 방법으로는 DNA, RNA, 단백질 subunit 또는 live attenuated 백신 등이 있다. 단백질 백신은 중화 항체보다는 빠르게 만들 수 있지만 제형을 개발하는데 시간이 소요되므로 이 단계에서 신속하게 만들 수 있는 RNA 백신이 Moderna와 CureVac을 통해서 임상시험이 시작되었다(Ref 8).
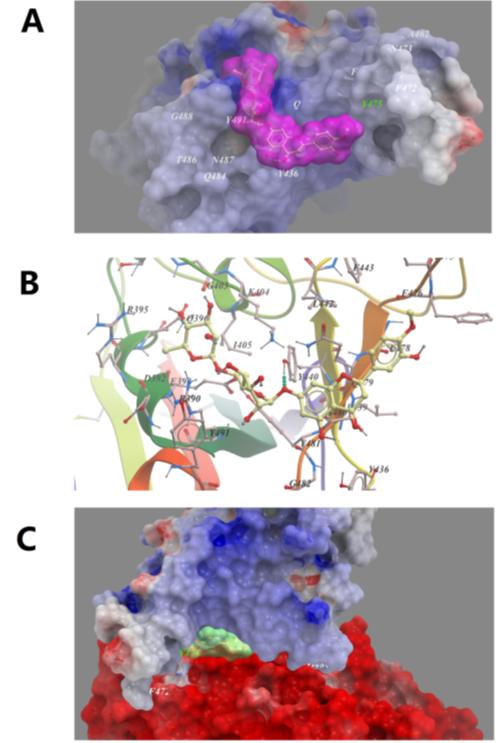
Figure 4. 분자 docking에 의해 산출된 hesperidin이 Spike RDB에 결합한 Low-energy binding conformation
(A) SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD 표면에 있는 얇은 포켓에 들어가 있다. (B) Spike RBD의 포켓에 hesperidin이 겹합한 상세도. (C) Hesperidin 이 ACE2 and Spike RBD 겹합 인터페이스를 막는다(Supporting PDB file SARS_CoV-2 _Spike_RBD_homo_Hesperidin.pdb) (Ref 1).
|
Company/group |
Technology |
Organization type |
|
Heat Biologics |
Cell-based |
Biotech |
|
Anges; Osaka University |
DNA vaccine |
Biotech; Academic |
|
Applied DNA Sciences; Takis Biotech |
DNA vaccine |
Biotech |
|
Inovio Pharmaceuticals; Beijing Advaccine Biotechnology |
DNA vaccine |
Biotech |
|
Zydus Cadila |
DNA vaccine; Live attenuated vaccine |
Biotech |
|
Codagenix; Serum Institute of India |
Live attenuated vaccine |
Biotech |
|
Institut Pasteur |
Live attenuated vaccine |
Academic |
|
AIM Vaccine |
Not disclosed |
Biotech |
|
Beijing Biological Products Institute (Sinopharm) |
Not disclosed |
Biotech |
|
Beijing Sanroad Biological Products |
Not disclosed |
Biotech |
|
Changchun Zhuoyi Biological |
Not disclosed |
Biotech |
|
China National Biotech Group (Sinopharm) |
Not disclosed |
Biotech |
|
Chongqing Zhifei Biological Products |
Not disclosed |
Biotech |
|
EpiVax; University of Georgia |
Not disclosed |
Biotech; Academic |
|
GC Pharma |
Not disclosed |
Biotech |
|
Hualan Biological Engineering |
Not disclosed |
Biotech |
|
ImmunoPrecise Antibodies; EVQLV |
Not disclosed |
Biotech |
|
Liaoning Chengda Biotechnology |
Not disclosed |
Biotech |
|
Minhai Biotechnology |
Not disclosed |
Biotech |
|
Royal (Wuxi) Bio-pharmaceutical |
Not disclosed |
Biotech |
|
Shenzhen Kangtai Biological Products |
Not disclosed |
Biotech |
|
Sinovac Biotech |
Not disclosed |
Biotech |
|
Walvax Biotechnology |
Not disclosed |
Biotech |
|
ZhongKe Biopharm |
Not disclosed |
Biotech |
|
Zhongyi Anke Biotechnology |
Not disclosed |
Biotech |
|
Institute of Medical Biology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences |
Not disclosed |
Academic |
|
University of Pittsburgh |
Not disclosed |
Academic |
|
Sanofi |
Protein-based |
Pharma/big biotech |
|
AJ Vaccines |
Protein-based |
Biotech |
|
Dynavax; University of Queensland |
Protein-based |
Biotech; Academic |
|
ExpreS2ion Biotech Holding |
Protein-based |
Biotech |
|
Generex Biotechnology; EpiVax |
Protein-based |
Biotech |
|
G+FLAS Life Sciences |
Protein-based |
Biotech |
|
iBio; Beijing CC-Pharming |
Protein-based |
Biotech |
|
Novavax; Emergent BioSolutions |
Protein-based |
Biotech |
|
Sichuan Clover Biopharmaceuticals |
Protein-based |
Biotech |
|
Sichuan University State Key Laboratory of Biotherapy; Zhejiang Teruisi Pharmaceutical; Chengdu National GLP Center; Sichuan Provincial People's Hospital; Chengdu Institute of Biological Products (Sinopharm) |
Protein-based |
Biotech; Academic |
|
Vaxil Bio |
Protein-based |
Biotech |
|
Baylor College of Medicine; University of Texas Medical Branch; New York Blood Center; Fudan University |
Protein-based |
Academic |
|
University of Saskatchewan |
Protein-based |
Academic |
|
Pfizer; BioNTech |
RNA vaccine |
Pharma/big biotech |
|
Arcturus Therapeutics; Duke-NUS Medical School |
RNA vaccine |
Biotech; Academic |
|
BioNTech; Fosun Pharma |
RNA vaccine |
Biotech |
|
CureVac |
RNA vaccine |
Biotech |
|
Moderna |
RNA vaccine |
Biotech |
|
Stermirna Therapeutics; Tongji University |
RNA vaccine |
Biotech; Academic |
|
Imperial College London |
RNA vaccine |
Academic |
|
MIGAL Galilee Research Institute |
Vector-based |
Academic |
|
Johnson & Johnson |
Viral vector |
Pharma/big biotech |
|
Altimmune |
Viral vector |
Biotech |
|
CanSino Biologics |
Viral vector |
Biotech |
|
GeoVax Labs; BravoVax |
Viral vector |
Biotech |
|
Greffex |
Viral vector |
Biotech |
|
Sumagen |
Viral vector |
Biotech |
|
Tonix Pharmaceuticals; Southern Research Institute |
Viral vector |
Biotech; Academic |
|
Vaxart |
Viral vector |
Biotech |
|
University of Oxford |
Viral vector |
Academic |
Table 2. 신규 COVID-19 백신 개발 동향 (Ref 9)
다음은 바이오 치료제인데, 항체의 경우는 코로나 바이러스의 Spike나 그 수용체인 ACE2를 타겟하고, RNA 치료제의 경우는 바이러스 지놈을 타겟할 수 있다. 하지만 이러한 타겟을 공략하는 치료제 개발전략은 Repurposing을 할 수 있는 특이적인 약물이 제한되어 있어 개발 후 임상에 소요되는 시간이 최소 1년 이상 예상된다.
|
Company/group |
Technology |
Organization type |
|
AbCellera Biologics; Eli Lilly |
Antibody |
Pharma/big biotech |
|
Takeda Pharmaceutical |
Antibody |
Pharma/big biotech |
|
Celltrion |
Antibody |
Biotech |
|
Emergent BioSolutions |
Antibody |
Biotech |
|
Eutilex |
Antibody |
Biotech |
|
GC Pharma |
Antibody |
Biotech |
|
Harbour BioMed; Mount Sinai |
Antibody |
Biotech; Academic |
|
ImmunoPrecise Antibodies; EVQLV |
Antibody |
Biotech |
|
Regeneron Pharmaceuticals |
Antibody |
Biotech |
|
Vir Biotechnology; WuXi Biologics |
Antibody |
Biotech |
|
Flanders Institute for Biotechnology (VIB); Ghent University |
Antibody |
Academic |
|
National Institutes of Health |
Antibody |
Academic |
|
Sorrento Therapeutics; Celularity |
Cell therapy |
Biotech |
|
NanoViricides |
Nanoparticle |
Biotech |
|
CEL-SCI Corporation |
Peptide |
Biotech |
|
Sirnaomics |
siRNA |
Biotech |
|
Vir Biotechnology; Alnylam Pharmaceuticals |
siRNA |
Biotech |
|
Enanta Pharmaceuticals |
Small molecule |
Biotech |
|
Insilico Medicine |
Small molecule |
Biotech |
|
RA Capital |
Small molecule |
Investor |
Table 3. 신규 COVID-19치료제 개발 동향 (Ref 9)
3) 면역회피 기전 및 면역조절
코로나19가 면역을 회피하는 경로를 살펴보자. Nsp1은 숙주의 40S ribosomal subunit과 반응하여 숙주 특이적인 mRNA 분해를 유도하고 type 1 인터페론 생산을 저해한다. Nsp3c는 숙주의 ADP-ribose에 결합하여 코로나19가 숙주의 선천면역에 저항할 수 있도록 한다. Bone marrow matrix antigen 2 (BST-2)는 숙주세포에서 새롭게 생성된 코로나 바이러스가 방출되는 단계를 저해할 수 있다. ORF7a는 직접 BST-2에 결합하여 BST-2의 glycosylation을 방해하여 그 활성을 저해한다. 이 단백질들도 잠재적으로 신약발굴의 타겟이 될 수 있다. 하지만 Repurposing 되는 약물은 없다.
앞에서 설명한 바이러스 복제과정에서의 면역회피 뿐만 아니라 바이러스에 대한 면역체계의 조절은 중요하다. 항바이러스제로 면역증강을 꾀하거나 중증환자에서 발생하는 cytokine storm을 피하고자 면역억제가 필요하다. 코로나 바이러스 치료제중 임상진행중인 Repurposing 약물의 목록을 보면 면역조절제인 인터페론 알파와 관절염에서 허가된 면역억제제/항염제인 IL-6에 대한 mAb인 Actemra (Tocilizumab)도 있다 (Table 4, Ref 10). Actemra는 중국에서 이미 코로나 19 치료제로 승인되었다. Genentech은 Actemra로 중증 코로나19 환자에 대한 임상 3상 시험을 신청하였다(Ref 11).
|
Drug or cocktail |
Originator company |
Status and mechanisms |
Clinical trials (trial posting date) |
|
ASC09/ritonavir, lopinavir/ritonavir, with or without umifenovir |
Ascletis, AbbVie, Pharmstandard |
ASC09 is an experimental HIV-1 protease inhibitor; ritonavir and lopinavir/ritonavir are approved protease inhibitors for HIV/AIDS; umifenovir is an approved entry inhibitor against influenza |
At least three trials (e.g., ChiCTR2000029603, 2/6/20) |
|
ASC09/oseltamivir, ritonavir/oseltamivir, oseltamivir |
Ascletis, Gilead, AbbVie |
See above; oseltamivir is a sialidase inhibitor approved for influenza |
One trial (NCT04261270, 2/7/20) |
|
Azvudine |
Zhengzhou Granlen PharmaTech |
Experimental reverse transcriptase inhibitor drug against HIV-1/AIDS |
One trial (ChiCTR2000029853, 2/15/20) |
|
Various combinations of baloxavir marboxil/favipiravir and lopinavir/ritonavir |
Shionogi, Toyama Chemical |
Baloxavir marboxil is a Cap-dependent endonuclease inhibitor and favipiravir is a guanine analog RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitor approved for influenza A and B; see above |
Two trials (ChiCTR2000029544, 2/3/20; ChiCTR2000029548, 2/4/20) |
|
Various combinations of darunavir/cobicistat alone or with lopinavir/ritonavir and thymosin α1 |
Janssen, Gilead |
Darunavir and cobicistat are, respectively, an HIV-1 protease inhibitor and inhibitor of cytochrome P450 (CYP)3A enzyme, approved as a combination against HIV-1/AIDS. Thymosin α1 is an immune response boosting agent |
Two trials (NCT04252274, 2/5/20; ChiCTR2000029541, 2/3/20) |
|
Remdesivir |
Gilead |
Phosphoramidate prodrug of an adenine analog used for Ebola and Marburg virus outbreaks (similar structure to approved HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitors) |
Two trials (NCT04252664, 2/5/20; NCT04257656, 2/6/20) |
|
Chloroquine or hydroxychloroquine |
Shanghai Zhongxi Pharmaceutical, Shanghai Ziyuan Pharmaceutical, Wuhan Wuyao Pharmaceutical |
Endosomal acidification fusion inhibitor |
At least ten trials (e.g., ChiCTR2000029826, 2/2/20; NCT04261517, 2/14/20) |
|
Methylprednisolone |
Generic |
Synthetic corticosteroid that binds to nuclear receptors to dampen proinflammatory cytokines |
One trial (NCT04263402, 2/10/20) |
|
Interferon alfa-2b alone or in combination with lopinavir/ritonavir and ribavirin |
Biogen, Merck |
Interferon alfa-2b is a recombinant cytokine with antiviral properties; ribavirin is a guanine derivative; as above |
Two trials (NCT04254874, 2/5/20; ChiCTR2000029308, 1/23/20) |
|
Camrelizumab and thymosin |
Incyte, Shanghai Hengrui Pharmaceutical |
Camrelizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody (mAb) targeting PD-1 |
Two trials (ChiCTR2000029806, 2/14/20; NCT04268537, 2/14/20) |
|
Tocilizumab |
Chugai Pharmaceutical, Zhejiang Hisun Pharmaceutical, Jiangsu Qyun Bio-Pharmaceutical |
Humanized mAb targeting interleukin-6 |
One trial (ChiCTR2000029765, 2/13/20) |
Table 4. COVID-19 치료를 위해 임상개발중인 Repurposed 된 치료제들 (Ref 10)
Ⅱ. 국내 치료제 개발 동향 및 승인절차
|
Repurposing(R)/new(N) |
Intervention |
Type |
Target |
개발전략 타겟유형 |
주관 |
Status |
비고 |
|
R |
Remdesvir |
Antiviral |
Ebola virus 치료제 (미승인) |
RdRp |
Gilead Korea (기업 주도) |
중등도 120명, 중증 75명 환자 2개 임상3상 진행중 (경북대 병원, 국립의료원, 서울의료원) 5월 발표 예정 |
중국 임상 3상 진행중 4월중 Topline 보고서 제출예정 |
|
서울대 병원 (연구자 주도) |
임상2상 진행중 (서울대병원, 보라매병원, 분당서울대병원) |
||||||
|
R |
Chloroquine |
|
말라리아 치료제 (승인) |
unknown |
아산병원 (연구자 주도) |
5월말 임상보고서 제출예정 |
|
|
R |
슈펙트 |
Anticancer |
혈액암 (승인) |
unknown |
일양약품 |
in vitro data 산출 |
|
|
R |
Rebovir |
Antiviral |
B형 간염 바이러스 ReverseTranscriptase 저해제 (승인) |
RdRp |
부광 |
in vitro data |
|
|
R |
Niclosamide
|
Antiparasitic
|
|
unknown |
한국파스퇴르연구소 |
In vitro data |
구충제 (미국승인). 흡수율이 낮아 제형변경 요구됨 |
|
R |
Ciclesonide |
Anti-allergic |
흡입용 코르티코스테로이드 (승인) |
Corona 19 NSP15 (riboendonuclease) |
한국파스퇴르연구소 |
In vitro data |
일본에서 3명 COVID-19 경증환자에서 약효 보임 |
|
N |
hzVSFv13주 |
Antiviral |
항바이러스제 (인플루엔자 임상 1상 시험중) |
unknown |
서울대병원 영남대병원 충남대병원
|
3개 병원에서 임상시험용 약품의 응급상황 사용 승인 획득 |
개발기업인 이뮨메드는 인플루엔자 치료용 임상 1상 진행중 |
|
N |
EBViNT |
T cell therapy |
항암제 (임상 1/2상 진행중) |
unknown |
유틸렉스 |
|
|
|
N |
퓨어스템 RA주 |
cell therapy |
immune modulation |
unknown |
강스템 |
영남대에서 임상시험용 약품의 응급상황 사용승인 신청중 (3/23 기준 미승인) |
|
|
|
|
siRNA |
바이러스 증식 억제 |
unknown |
바이오니아 |
선도물질 도출 |
|
|
|
|
항체 |
|
Spike protein |
셀트리온 |
후보항체 300종 확보, 중화항체 선별중, 항체치료제 개발 트랙을 따라갈 예정 |
|
|
|
|
단백질 백신 |
|
Spike protein |
SK 바이오사이언스 |
후보물질 발현, 동물실험 개시 |
|
|
|
|
백신 |
|
2? 구체적 내용 확인 어려움 |
GC녹십자 |
|
|
|
|
|
DNA 백신 |
|
2? 구체적 내용 확인 어려움 |
제넥신 |
|
|
Table 5. 국내기업 개발 동향
코로나 19 치료제 국내 개발 동향은 뉴스 검색을 통해 확인 가능한 물질들을 대상으로 정리하였으며(2020년 3월 23일 기준), 해당 기업이 제시하는 작용기전을 본 보고서에서 채택한 개발전략과 타겟 유형에 따라 해당 내용을 표시했다. 다만 작용기전이나 제시하는 타겟이 불분명할 경우는 unknown으로 표시하였다(Table 5).
보통 코로나 19와 같은 위급한 상황에서 임상시험용 의약품의 동정적 사용제도는 약사법 제34조 제4항에 따라 허용되고 있다. 그 절차는 식약처장의 사용승인을 위해 신청하는 주체 및 대상환자 규모에 따라 2종류로 나뉘며 “의약품 등의 안전에 관한 규칙’ 제28조에서 규정하고 있다. 첫 번째로 (1) 환자의 주치의가 개인별 환자의 치료를 위해 임상시험용 의약품의 사용승인을 신청하는 경우와 두 번째 경우는 (2) 제약기업이 임상 시험결과 안전성, 유효성이 관찰된 의약품을 시판허가를 받기 전에 환자치료를 위해 다수의 환자에게 사용하기 위해 사용신청을 하는 경우이다. 환자의 응급상황 사용은 연구자(의료진 등) 주도로, 치료목적의 임상의 경우는 다수의 환자를 대상으로 기업주도로 이뤄진다. 이 두 경우 모두 제약회사가 무상으로 의약품을 제공하게 된다. 응급상황 사용의 경우, 환자의 자발적인 동의서가 있어야 신청 가능하고 임상시험 의약품을 사용하다가 대상 환자에게 발생한 예상하지 못한 중대한 이상반응에 대하여는 ‘임상시험 관리 기준’에 따라 식약처장에게 보고하여야 한다(Ref 12, 13).
또한 해외에서 코로나19에 대한 신약이 승인되면 이를 긴급 수입하는 절차도 있다.<끝>
참고문헌
Wu C. et al. Analysis of therapeutic targets for SARS-CoV-2 and discovery of potential drugs by computational methods. 2020 Feb Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B
First up for COVID-19: nearly 30 clinical readouts before end of April. Biocentury 2020. March 14. https://www.biocentury.com/article/304658/nearly-30-trials-for-covid-19-could-start-to-yield-data-in-the-next-couple-of-months
https://www.theguardian.com/world/2020/mar/18/japanese-flu-drug-clearly-effective-in-treating-coronavirus-says-china
Cao B. er al. A Trial of Lopinavir–Ritonavir in Adults Hospitalized with Severe Covid-19. NEJM 2020. March 18.
Wang M. et al. Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro. Cell Research 2020. 30:269–271
Wrapp D. et al. Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV Spike in the prefusion conformation. 2020. Science, 367. 1260-1263
Hoffman et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and IS Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. 2020. Cell 181, 1-10
https://www.nytimes.com/2020/03/16/health/coronavirus-vaccine.html
COVID-19: A growing list of new vaccines and therapies in development. Biocentury 2020. Feb. 26. https://www.biocentury.com/article/304515
Harrison C. Coronavirus puts drug repurposing on the fast track. 2020 Nature Biotechnology Feb 27
https://www.genengnews.com/virology/coronavirus/genentech-launches-phase-iii-trial-of-actemra-as-coronavirus-treatment/
식약처 보도자료, ‘응급환자 등 치료를 위한 임상시험용의약품의 안전 사용 가이드라인’ 발간 2015.12.30
식약처 의약품안전국 임상제도과. 임상시험용의약품의 치료목적사용을 위한 가이드라인. 2018,4